
Once the IDE itself is installed, the developer may still need to download and install various libraries and project dependencies. To get started using a local IDE, a developer needs to download and install the IDE, which may be as simple as launching a binary file or it may involve many complicated steps and terminal commands. Another common choice is Eclipse, which is primarily used for Java development but which now supports many other languages as well. Exact market share numbers are difficult to determine, especially because some surveys lump together Visual Studio and VS Code while others separate them, but estimates suggest that Microsoft controls anywhere from 28% to over 40% of the market. The current reigning champion of local IDEs is Microsoft Visual Studio. Installing and running your preferred IDE locally is the most common way of working for developers. In this post, we will lay out some of the fundamental differences between using a local IDE versus a cloud-based IDE and explore some scenarios where you might prefer one over the other. We’ve written before about some of the advantages of cloud-based development as well as some of the roadblocks that have prevented more developers from moving to the cloud. In the last few years there has been a growing interest in moving development workspaces and IDEs to the cloud. Traditionally, developers have run their IDEs on their local machines. The best IDEs are tightly integrated, allowing developers to work quickly without requiring them to switch between different applications to complete tasks. In many cases, this can happen in real-time as the developer is typing. Debugger: a debugger is a tool for identifying errors in the source code.
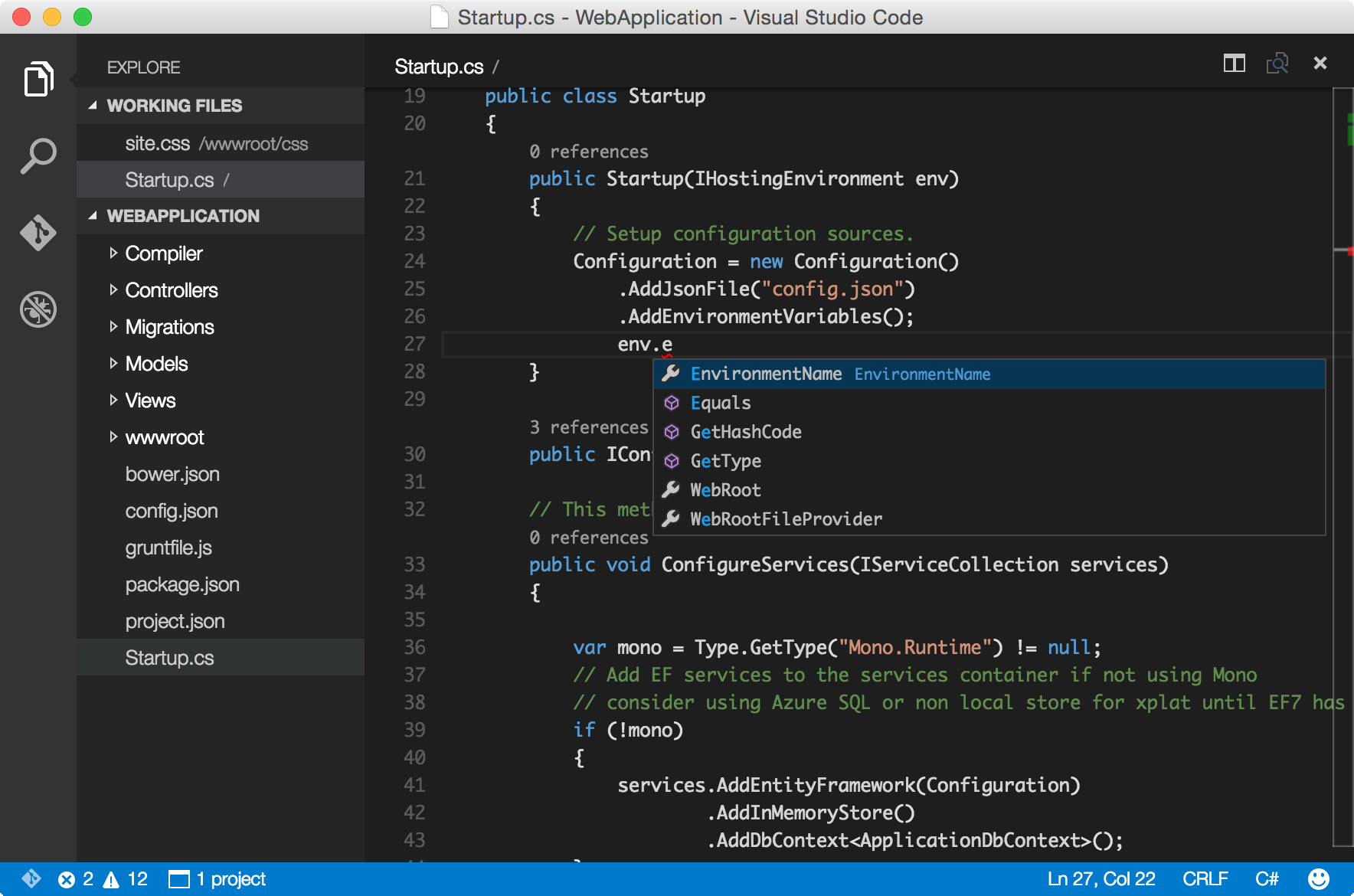
These tasks may encompass several tasks including documentation, testing, compilation, and distribution of the binary software code. Build automation tools: these tools take the written code and, through a series of automated tasks, turn it into code that can be executed and run on a machine.
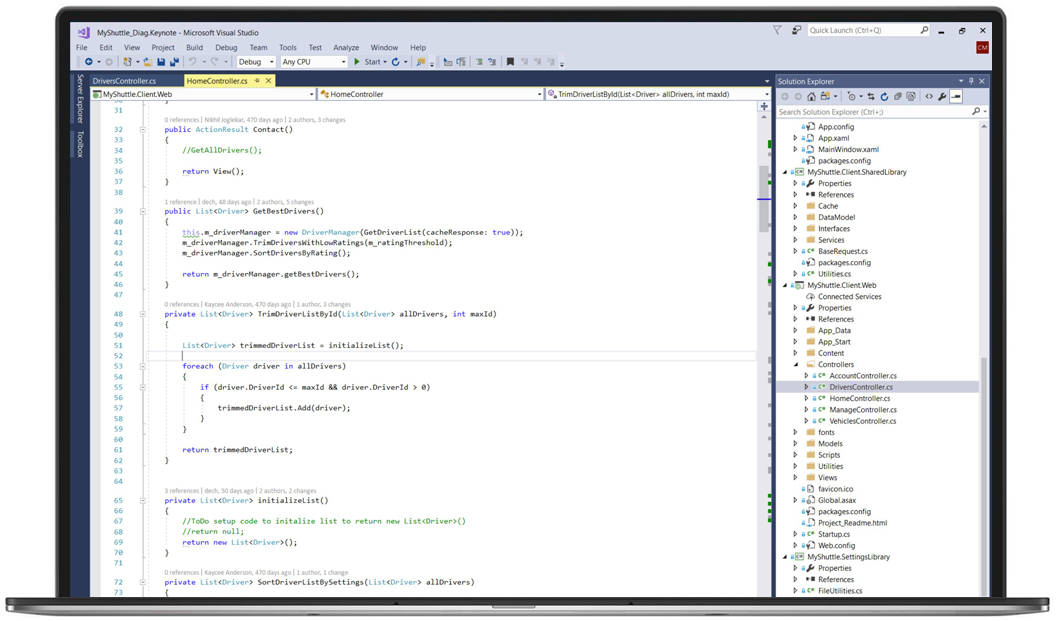
In its most basic form, this is a text editor, but most editors include features such as syntax highlighting and autocompletion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
